Visibility Improvement
Shadow Illumination and Single Image Super Resolution for Visibility Improvement
When processing WAMI (Wide Area Motion Imagery) data several preprocessing techniques can be applied to significantly improve the visibility of the imagery. The objective of this research is to improve visibility in low/non-uniform lighting conditions for wide area surveillance applications and to enhance features to improve the performance of automatic object detection/tracking/recognition algorithms on wide area surveillance data. Although in most cases the human eye can observe the enhancement of the imagery, we demonstrate the improvement in usability of data by comparing the results of key feature points extraction methods. We analyze the improvements in the number and quality of feature points extracted before and after the visibility improvement technique is applied.
We utilize two key point extractors, Harris Corner Detection and the Speeded Up Robust Features (SURF), on the original frame and processed frame to evaluate the effects of the visibility improvement technique. A key feature point can be defined as a point where there are two dominant and different edge directions in a local neighborhood of the point. These points are used in image registration, an essential step in the wide area object tracking process. Key interest point detectors are also used in Video Stabilization, 3D Scene Creation and Object Classification.
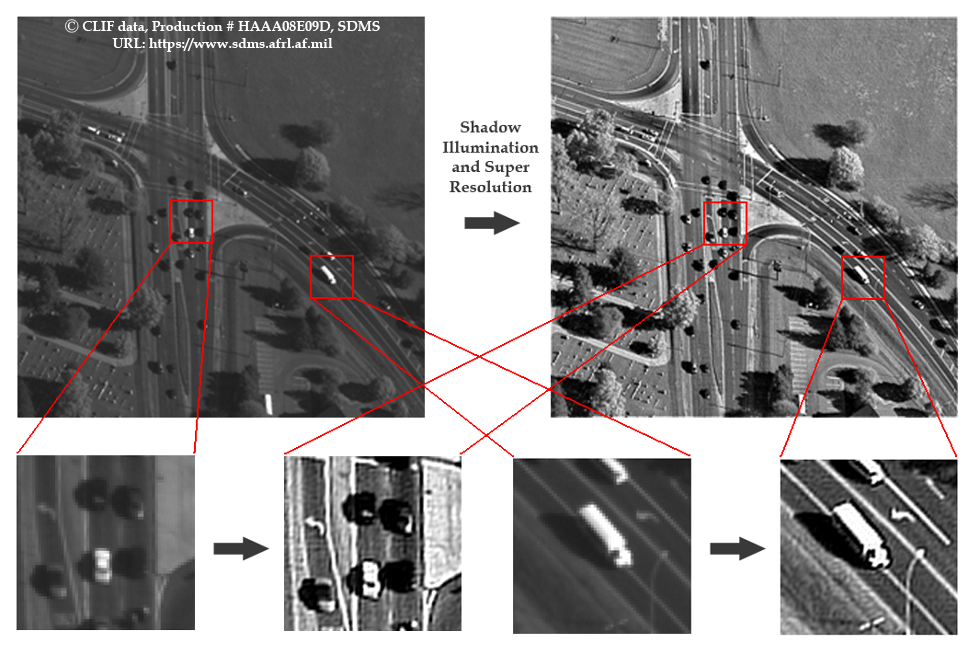
The image on the right illustrates a cropped downsampled wide area frame take from airplane. When scrolling over the image the results of the visibility improvement technique appear. The visibility improvement technique consists of two major preprocessing steps. 1) Nonlinear Neighborhood Dependant Image Enhancement and 2) Single Image Super Resolution.
Shadow Illumination
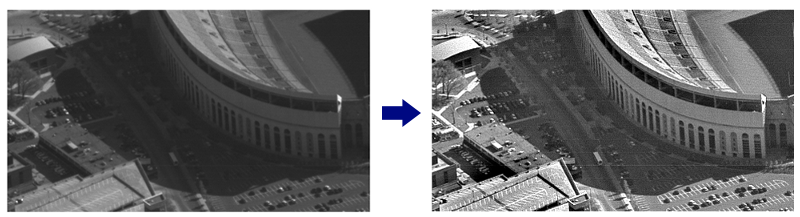
In this nonlinear image enhancement process, we simultaneously illuminate dark shadowy regions of the scene as well as compress (dim) over-exposed regions. In the images below, the results of this process can be observed. Note the improved visibility in the shadowy region of the parking lot.
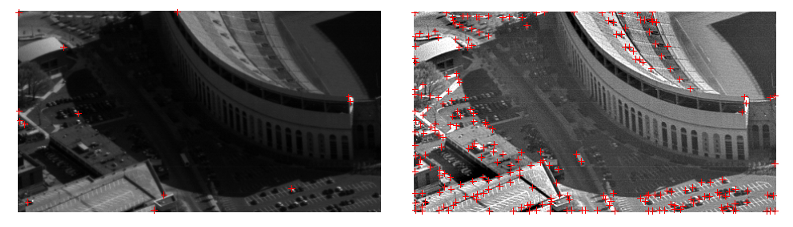
We measure the improvement in image quality by comparing the results of a key point feature extraction algorithm on the two images. The results of the Harris Corner Detector applied to the two images above are shown below.
Single Image Super Resolution
In this nonlinear interpolation process, we increase the resolution of the input frame by scale of sixteen. An N x M image becomes a 4N x 4M image. As a result of this process, objects in the scene that were previously described by 40 pixel intensities (4x10 pixel is an average size of a vehicle in WAMI data) is now described by 640 pixel intensities. With more resolution, more feature points are extracted, and as a result better classification and recognition of objects occurs. The image below illustrates the effects of super resolution and shadow illumination. Note the increased visibility on the roads as well as the vehicles in the scene.